Myeloid adverse primary acknowledgment gene (88) (MYD88) is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the MYD88 gene.
Function
The animal ortholog MYD88 seems to action analogously to mice, back the immunological phenotype of animal beef amiss in MYD88 is agnate to beef from MyD88 amiss mice. However, accessible affirmation suggests that MYD88 is disposable for animal attrition to accepted viral infections and to all but a few pyogenic bacterial infections, demonstrating a above aberration amid abrasion and animal allowed responses.
MyD88 Homodimerization Inhibitory Peptide Set Functions as a decoy by binding to the MyD88 TIR domain.
MyD88 Homodimerization Inhibitory Peptide Set encodes a cytosolic adapter protein that plays a central role in the innate and adaptive immune response.This protein functions as an essential signal transducer in the interleukin-1 and Toll-like receptor signaling pathways. These pathways regulate that activation of numerous proinflammatory genes. The encoded protein consists of an N-terminal death domain and a C-terminal Toll-interleukin1 receptor domain. Patients with defects in this gene have an increased susceptibility to pyogenic bacterial infections. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants.
More about: MyD88 Homodimerization Inhibitory Peptide Set sale
Read more: Medicine raw materials
Medicine raw materials,Pharmaceuticals ,Advanced chemicla ,Assay-kits,Proteins,APIs
Saturday, March 31, 2012
Thursday, March 29, 2012
What is 2-Chloro-N,N-dimethylacetamide?
2-Chloro-N,N-dimethylacetamide
CAS:2675-89-0
Molecular Formula:C4H8ClNO
Formula Weight:121.57
Specification:1g/250mg
Dimethylacetamide is the amoebic admixture with the blueprint CH3C(O)N(CH3)2. This colorless, baptize miscible, top baking aqueous is frequently acclimated as a arctic bread-and-butter in amoebic chemistry. DMAc is miscible with a lot of added solvents, although it is ailing acrid in aliphatic hydrocarbons.
The actinic reactions of dimethylacetamide are archetypal of N,N-disubstituted amides. It will hydrolyze in the attendance of acids:
CH3CON(CH3)2 + H2O + HCl → CH3COOH + (CH3)2NH2+Cl-
Dimethylacetamide is advantageous as a average for able bases such as sodium hydroxide. Dimethylacetamide is frequently acclimated as a bread-and-butter for fibers or in the adhering industry. It is aswell active in the assembly of pharmaceuticals and plasticizers as a acknowledgment medium.
More about: 2-Chloro-N,N-dimethylacetamide sale
Read more: Reagents
CAS:2675-89-0
Molecular Formula:C4H8ClNO
Formula Weight:121.57
Specification:1g/250mg
Dimethylacetamide is the amoebic admixture with the blueprint CH3C(O)N(CH3)2. This colorless, baptize miscible, top baking aqueous is frequently acclimated as a arctic bread-and-butter in amoebic chemistry. DMAc is miscible with a lot of added solvents, although it is ailing acrid in aliphatic hydrocarbons.
The actinic reactions of dimethylacetamide are archetypal of N,N-disubstituted amides. It will hydrolyze in the attendance of acids:
CH3CON(CH3)2 + H2O + HCl → CH3COOH + (CH3)2NH2+Cl-
Dimethylacetamide is advantageous as a average for able bases such as sodium hydroxide. Dimethylacetamide is frequently acclimated as a bread-and-butter for fibers or in the adhering industry. It is aswell active in the assembly of pharmaceuticals and plasticizers as a acknowledgment medium.
More about: 2-Chloro-N,N-dimethylacetamide sale
Read more: Reagents
Wednesday, March 28, 2012
What is MyD88 Homodimerization Inhibitory Peptide Set?
Pepinh-MYD is a 26 aa peptide that blocks MyD88 signaling by inhibiting its homodimerization through binding. Pepinh-MYD contains a arrangement from the MyD88 TIR homodimerization area (RDVLPGT) preceeded by a protein transduction arrangement (RQIKIWFQNRMKWKK) acquired from antennapedia which enables the peptide to translocate through the corpuscle film. Pepinh-MYD is provided with Pepinh-Control, a ascendancy peptide.
Myeloid differentiation primary response gene (88) (MYD88) is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the MYD88 gene
Function
The animal ortholog MYD88 seems to action analogously to mice, back the immunological phenotype of animal beef amiss in MYD88 is agnate to beef from MyD88 amiss mice. However, accessible affirmation suggests that MYD88 is disposable for animal attrition to accepted viral infections and to all but a few pyogenic bacterial infections, demonstrating a above aberration amid abrasion and animal allowed responses.
Myd88 has been shown to interact with TLR 4, Interleukin 1 receptor, type I, RAC1, IRAK2 and IRAK1.
More about: MyD88 Homodimerization Inhibitory Peptide Set sale
Read more: Medicine raw materials
Myeloid differentiation primary response gene (88) (MYD88) is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the MYD88 gene
Function
The animal ortholog MYD88 seems to action analogously to mice, back the immunological phenotype of animal beef amiss in MYD88 is agnate to beef from MyD88 amiss mice. However, accessible affirmation suggests that MYD88 is disposable for animal attrition to accepted viral infections and to all but a few pyogenic bacterial infections, demonstrating a above aberration amid abrasion and animal allowed responses.
Myd88 has been shown to interact with TLR 4, Interleukin 1 receptor, type I, RAC1, IRAK2 and IRAK1.
More about: MyD88 Homodimerization Inhibitory Peptide Set sale
Read more: Medicine raw materials
Tuesday, March 27, 2012
Uses of Ethyl acetate
Ethyl acetate is the most familiar ester to many chemistry students and possibly the ester with the widest range of uses. Esters are structurally derived from carboxylic acids by replacing the acidic hydrogen by an alkyl or aryl group. Ethyl acetate itself is a colourless liquid at room temperature with a pleasant "fruity" smell, b.p. 77°C.
Ethyl acetate (systematically, ethyl ethanoate, commonly abbreviated EtOAc or EA) is the organic compound with the formula CH3COOCH2CH3. This colorless liquid has a characteristic sweet smell (similar to pear drops) and is used in glues, nail polish removers, and cigarettes (see list of additives in cigarettes). Ethyl acetate is the ester of ethanol and acetic acid; it is manufactured on a large scale for use as a solvent. The combined annual production in 1985 of Japan, North America, and Europe was about 400,000 tons. In 2004, an estimated 1.3M tons were produced worldwide.
Uses
Ethyl acetate has many uses, such as artificial fruit essences and aroma enhancers, artificial flavours for confectionery, ice cream and cakes, as a solvent in many applications (including decaffeinating tea and coffee) for varnishes and paints (nail varnish remover), and for the manufacture of printing inks and perfumes.
Ethyl acetate is used primarily as a solvent and diluent, being favored because of its low cost, low toxicity, and agreeable odor. For example, it is commonly used to clean circuit boards and in some nail varnish removers (acetone and acetonitrile are also used). Coffee beans and tea leaves are decaffeinated with this solvent. It is also used in paints as an activator or hardener. Ethyl acetate is present in confectionery, perfumes, and fruits. In perfumes, it evaporates quickly, leaving only the scent of the perfume on the skin.
More about: Ethyl acetate sale
Read more: Reagents
Ethyl acetate (systematically, ethyl ethanoate, commonly abbreviated EtOAc or EA) is the organic compound with the formula CH3COOCH2CH3. This colorless liquid has a characteristic sweet smell (similar to pear drops) and is used in glues, nail polish removers, and cigarettes (see list of additives in cigarettes). Ethyl acetate is the ester of ethanol and acetic acid; it is manufactured on a large scale for use as a solvent. The combined annual production in 1985 of Japan, North America, and Europe was about 400,000 tons. In 2004, an estimated 1.3M tons were produced worldwide.
Uses
Ethyl acetate has many uses, such as artificial fruit essences and aroma enhancers, artificial flavours for confectionery, ice cream and cakes, as a solvent in many applications (including decaffeinating tea and coffee) for varnishes and paints (nail varnish remover), and for the manufacture of printing inks and perfumes.
Ethyl acetate is used primarily as a solvent and diluent, being favored because of its low cost, low toxicity, and agreeable odor. For example, it is commonly used to clean circuit boards and in some nail varnish removers (acetone and acetonitrile are also used). Coffee beans and tea leaves are decaffeinated with this solvent. It is also used in paints as an activator or hardener. Ethyl acetate is present in confectionery, perfumes, and fruits. In perfumes, it evaporates quickly, leaving only the scent of the perfume on the skin.
More about: Ethyl acetate sale
Read more: Reagents
Sunday, March 25, 2012
Specifications of Methyl Linoleat
Methyl Linoleat
CAS:112-63-0
Molecular Formula:C19H34O2
Formula Weight:294.47
Description
Synonym: Linoleic acid methyl ester
Specification:1g
Melting point:?35 °C(lit.)
Boiling point:192 °C4 mm Hg(lit.)
Physical Appearance: clear colorless liquid
Storage:Refrigerate in tightly sealed containers.
Linoleic acid (LA) is an unsaturated n-6 fatty acid. It is a colorless liquid at room temperature. In physiological literature, it has a lipid number of 18:2(n-6). Chemically, linoleic acid is a carboxylic acid with an 18-carbon chain and two cis double bonds; the first double bond is located at the sixth carbon from the methyl end.
Linoleic acid belongs to one of the two families of essential fatty acids that humans and animals must ingest for good health, because the body requires them for various biological processes, but cannot synthesize them from other food components.
More about: Methyl Linoleat sale
Read more: reagent
CAS:112-63-0
Molecular Formula:C19H34O2
Formula Weight:294.47
Description
Synonym: Linoleic acid methyl ester
Specification:1g
Melting point:?35 °C(lit.)
Boiling point:192 °C4 mm Hg(lit.)
Physical Appearance: clear colorless liquid
Storage:Refrigerate in tightly sealed containers.
Linoleic acid (LA) is an unsaturated n-6 fatty acid. It is a colorless liquid at room temperature. In physiological literature, it has a lipid number of 18:2(n-6). Chemically, linoleic acid is a carboxylic acid with an 18-carbon chain and two cis double bonds; the first double bond is located at the sixth carbon from the methyl end.
Linoleic acid belongs to one of the two families of essential fatty acids that humans and animals must ingest for good health, because the body requires them for various biological processes, but cannot synthesize them from other food components.
More about: Methyl Linoleat sale
Read more: reagent
Uses of Sodium polyphosphate
Sodium polyphosphate
CAS:68915-31-1
Molecular Formula:Na3O10P3X2
Formula Weight:321.88
Description:
Appearance:Colourless glassy spicules.
Solubility: Readily souble in water, insouble in organic solvents.
Use:Used as water softener for boiler water and industry water.
Storage:In ventilate,cool and dry places.
Sodium polyphosphate are used as an acidity regulator, emulsifier, humectant, raising agent, sequestrant, stabilizer, thickener. It is coded as E452 (i) by the European Union. Sodium Metaphosphate, Sodium tetrapolyphosphate and Sodium Hexametaphosphate are all sodium polyphosphates. It is used in detergent and in toothpaste manufacturing, ceramic manufacturing and cosmetics. It is used in breakfast cereals, ice cream, ice milk, bottled beverages, reconstituted lemon juice, puddings, processed cheeses, artificially sweetened jellies, meat, poultry, sea foods, and pet foods. It is a skin irritant and causes kidney damage.
Phosphates have the ability to sequester calcium and it may form calcium phosphate so it poses some risk to people with kidney stones. Sodium metaphosphate leads to growth retardation in rats. It is used as an oral care agent. Sodium polyphosphates induce kidney damage and act as a skin irritant. Irritation is a function of concentration. It leads to the enlargement of parathyroid glands*. It may cause gastrointestinal tract irritation and may cause nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. High concentrations of phosphates may disturb several metabolic processes as phosphate plays an important role in general metabolism.
More about: Sodium polyphosphate sale
Read more: Reagents chemical
Thursday, March 22, 2012
What is Antimony potassium tartrate?
Antimony potassium tartrate is used as a mordant or fixing agent in the leather and textile dying as well as an analytical reagent and a flux additive for electoplating. It is used in making insecticides or pesticides. It was used as a parasiticide or as an emetic and expectorant.
Antimony is a semi-metallic chemical element in Group Va of the periodic table. It is a poor conductor of heat and electricity and is easily powdered to be used by itself. The chief ore of antimony is stibnite (Sb2S3, antimony trisulfide) which is produced in China and covers three-fourths of the world's mined antimony. It is also found in isomorphous mixture with arsenic, as allemonite. Substantial quantity of antimony are produced as a by-product in the smelting of base metal ores also. The pure antimony is produced from the ore by roasting it to form the oxide, then reducing the oxide with carbon or iron. Antimony is soluble in hot nitric or sulfuric acid and reacts with oxidizing acids and halogens (fluorine, chlorine, or bromine).
Antimony potassium tartrate is white crystalline powder with a sweetish taste It is used as a mordant or fixing agent in the leather and textile dying as well as an analytical reagent and flux additive for electoplating. It is used in making insecticides or pesticides. It was used as a parasiticide or as an emetic and expectorant.
More about: Antimony potassium tartrate sale
Read more: Reagents
Antimony is a semi-metallic chemical element in Group Va of the periodic table. It is a poor conductor of heat and electricity and is easily powdered to be used by itself. The chief ore of antimony is stibnite (Sb2S3, antimony trisulfide) which is produced in China and covers three-fourths of the world's mined antimony. It is also found in isomorphous mixture with arsenic, as allemonite. Substantial quantity of antimony are produced as a by-product in the smelting of base metal ores also. The pure antimony is produced from the ore by roasting it to form the oxide, then reducing the oxide with carbon or iron. Antimony is soluble in hot nitric or sulfuric acid and reacts with oxidizing acids and halogens (fluorine, chlorine, or bromine).
Antimony potassium tartrate is white crystalline powder with a sweetish taste It is used as a mordant or fixing agent in the leather and textile dying as well as an analytical reagent and flux additive for electoplating. It is used in making insecticides or pesticides. It was used as a parasiticide or as an emetic and expectorant.
More about: Antimony potassium tartrate sale
Read more: Reagents
Wednesday, March 21, 2012
Are you searching Cytochrome P450 1B1 (human) Yeast Reductase?
Cytochrome P450 is a family of the body's more powerful detox enzymes. Over 60 key forms are known, with hundreds of genetic variations possible, producing a wide variety of susceptibility to specific toxins. As the saying goes, "One man's meat is another man's poison".
The cytochrome P450 superfamily (officially abbreviated as CYP) is a large and diverse group of enzymes. The function of most CYP enzymes is to catalyze the oxidation of organic substances. The substrates of CYP enzymes include metabolic intermediates such as lipids and steroidal hormones, as well as xenobiotic substances such as drugs and other toxic chemicals. CYPs are the major enzymes involved in drug metabolism and bioactivation, accounting for about 75% of the total number of different metabolic reactions.
Cytochrome P450 (CYPs) belong to the superfamily of proteins containing a heme cofactor and, therefore, are hemoproteins. CYPs use a variety of small and large molecules as substrates in enzymatic reactions. Often, they form part of multi-component electron transfer chains, called P450-containing systems. Cytochromes P450 have been named on the basis of their cellular (cyto) location and spectrophotometric characteristics (chrome): when the reduced heme iron forms an adduct with CO, P450 enzymes absorb light at wavelengths near 450 nm, identifiable as a characteristic Soret peak.
CYP enzymes have been identified in all domains of life, i.e., in animals, plants, fungi, protists, bacteria, archaea, and even viruses. More than 11,500 distinct CYP proteins are known.
Human CYPs are primarily membrane-associated proteins[12] located either in the inner membrane of mitochondria or in the endoplasmic reticulum of cells. CYPs metabolize thousands of endogenous and exogenous chemicals. Some CYPs metabolize only one (or a very few) substrates, such as CYP19 (aromatase), while others may metabolize multiple substrates. Both of these characteristics account for their central importance in medicine. Cytochrome P450 enzymes are present in most tissues of the body, and play important roles in hormone synthesis and breakdown (including estrogen and testosterone synthesis and metabolism), cholesterol synthesis, and vitamin D metabolism. Cytochrome P450 enzymes also function to metabolize potentially toxic compounds, including drugs and products of endogenous metabolism such as bilirubin, principally in the liver.
The Human Genome Project has identified 57 human genes coding for the various cytochrome P450 enzymes.
More about: Cytochrome P450 1B1 (human) Yeast Reductase sale
Read more: Medicine raw materials
The cytochrome P450 superfamily (officially abbreviated as CYP) is a large and diverse group of enzymes. The function of most CYP enzymes is to catalyze the oxidation of organic substances. The substrates of CYP enzymes include metabolic intermediates such as lipids and steroidal hormones, as well as xenobiotic substances such as drugs and other toxic chemicals. CYPs are the major enzymes involved in drug metabolism and bioactivation, accounting for about 75% of the total number of different metabolic reactions.
Cytochrome P450 (CYPs) belong to the superfamily of proteins containing a heme cofactor and, therefore, are hemoproteins. CYPs use a variety of small and large molecules as substrates in enzymatic reactions. Often, they form part of multi-component electron transfer chains, called P450-containing systems. Cytochromes P450 have been named on the basis of their cellular (cyto) location and spectrophotometric characteristics (chrome): when the reduced heme iron forms an adduct with CO, P450 enzymes absorb light at wavelengths near 450 nm, identifiable as a characteristic Soret peak.
CYP enzymes have been identified in all domains of life, i.e., in animals, plants, fungi, protists, bacteria, archaea, and even viruses. More than 11,500 distinct CYP proteins are known.
Human CYPs are primarily membrane-associated proteins[12] located either in the inner membrane of mitochondria or in the endoplasmic reticulum of cells. CYPs metabolize thousands of endogenous and exogenous chemicals. Some CYPs metabolize only one (or a very few) substrates, such as CYP19 (aromatase), while others may metabolize multiple substrates. Both of these characteristics account for their central importance in medicine. Cytochrome P450 enzymes are present in most tissues of the body, and play important roles in hormone synthesis and breakdown (including estrogen and testosterone synthesis and metabolism), cholesterol synthesis, and vitamin D metabolism. Cytochrome P450 enzymes also function to metabolize potentially toxic compounds, including drugs and products of endogenous metabolism such as bilirubin, principally in the liver.
The Human Genome Project has identified 57 human genes coding for the various cytochrome P450 enzymes.
More about: Cytochrome P450 1B1 (human) Yeast Reductase sale
Read more: Medicine raw materials
Tuesday, March 20, 2012
What is Testosterone-17-acetate?
Testosterone-17-acetate
SYNONYMS Deposteron;17beta-Acetoxy-4-androsten-3-one; 4-Androsten-17b-ol-3-one 17-acetate; 17beta-Hydroxy-4-androsten-3-one 17-acetate;
CAS:1045-69-8
Molecular Formula:C21H30O3
Formula Weight:330.46
PHYSICAL STATE white to off-white crystalline powder
MELTING POINT 139 - 141 C
Testosterone is the major androgenic hormone that is responsible for the growth and development of masculine characteristics. It is produced in the Leydig cells (interstitial cells) of the testes. it regulates gonadotropic secretion and wolffian duct differentiation (formation of the epididymis, vas deferens, and seminal vesicle), and stimulates skeletal muscle. It is also responsible for other male characteristics and spermatogenesis after its conversion to dihydrotestosterone by 5alpha-reductase in peripheral tissue. Testosterone is converted to dihydrotestosterone in the target tissues where it appears to mediate many of the biological actions of testosterone. In addition, testosterone possesses protein anabolic properties, manifested by retention of nitrogen, calcium, phosphorus, and potassium, and is important in maintaining muscle mass and bone tissue in the adult male. It is also converted by aromatization to estradiol in peripheral tissue. It has been synthesized for replacement therapy, in the form of various esters having prolonged duration of effects, in treating male hypogonadism, cryptorchidism, frigidity, inoperable female breast cancer, oligospermia, to suppress lactation, and as an anabolic agent. Esters administered by subcutaneous, intramuscular injection, buccally or intramuscularly include;
More about: Testosterone-17-acetate sale
Read more: Reagents
SYNONYMS Deposteron;17beta-Acetoxy-4-androsten-3-one; 4-Androsten-17b-ol-3-one 17-acetate; 17beta-Hydroxy-4-androsten-3-one 17-acetate;
CAS:1045-69-8
Molecular Formula:C21H30O3
Formula Weight:330.46
PHYSICAL STATE white to off-white crystalline powder
MELTING POINT 139 - 141 C
Testosterone is the major androgenic hormone that is responsible for the growth and development of masculine characteristics. It is produced in the Leydig cells (interstitial cells) of the testes. it regulates gonadotropic secretion and wolffian duct differentiation (formation of the epididymis, vas deferens, and seminal vesicle), and stimulates skeletal muscle. It is also responsible for other male characteristics and spermatogenesis after its conversion to dihydrotestosterone by 5alpha-reductase in peripheral tissue. Testosterone is converted to dihydrotestosterone in the target tissues where it appears to mediate many of the biological actions of testosterone. In addition, testosterone possesses protein anabolic properties, manifested by retention of nitrogen, calcium, phosphorus, and potassium, and is important in maintaining muscle mass and bone tissue in the adult male. It is also converted by aromatization to estradiol in peripheral tissue. It has been synthesized for replacement therapy, in the form of various esters having prolonged duration of effects, in treating male hypogonadism, cryptorchidism, frigidity, inoperable female breast cancer, oligospermia, to suppress lactation, and as an anabolic agent. Esters administered by subcutaneous, intramuscular injection, buccally or intramuscularly include;
More about: Testosterone-17-acetate sale
Read more: Reagents
Monday, March 19, 2012
What bis Cytochrome P450 1B1 (human) Yeast Reductase?
Description of Cytochrome P450 1B1 (human) Yeast Reductase
Human cytochrome P450 1B1 (CYP1B1) is found mainly in extrahepatic tissues and is overexpressed in a array of animal tumors. Metabolic activation of 17β-estradiol (E2) to 4-hydroxy E2 by CYP1B1 has been accepted to be an important agency in mammary carcinogenesis. The inhibition of recombinant animal CYP1B1 by 2,2′,4,6′-tetramethoxystilbene (TMS) was advised application either the Escherichia coli membranes of recombinant animal CYP1B1 coexpressed with animal NADPH-P450 reductase or application antiseptic enzyme. 2,2′,4,6′-TMS showed almighty and careful inhibition of ethoxyresorufin O-deethylation (EROD) action of CYP1B1 with IC50 ethics of 2 nM. 2,2′,4,6′-TMS apparent 175-fold selectivity for CYP1B1 over CYP1A1 (IC50, 350 nM) and 85-fold selectivity for CYP1B1 over CYP1A2 (IC50, 170 nM). However, inhibition of animal NADPH-P450 reductase action by 2,2′,4,6′-TMS was negligible. The modes of inhibition by 2,2′,4,6′-TMS were noncompetitive for CYP1A1 and CYP1B1.
More about: Cytochrome P450 1B1 (human) Yeast Reductase sale
Read more: Medicine raw materials
Human cytochrome P450 1B1 (CYP1B1) is found mainly in extrahepatic tissues and is overexpressed in a array of animal tumors. Metabolic activation of 17β-estradiol (E2) to 4-hydroxy E2 by CYP1B1 has been accepted to be an important agency in mammary carcinogenesis. The inhibition of recombinant animal CYP1B1 by 2,2′,4,6′-tetramethoxystilbene (TMS) was advised application either the Escherichia coli membranes of recombinant animal CYP1B1 coexpressed with animal NADPH-P450 reductase or application antiseptic enzyme. 2,2′,4,6′-TMS showed almighty and careful inhibition of ethoxyresorufin O-deethylation (EROD) action of CYP1B1 with IC50 ethics of 2 nM. 2,2′,4,6′-TMS apparent 175-fold selectivity for CYP1B1 over CYP1A1 (IC50, 350 nM) and 85-fold selectivity for CYP1B1 over CYP1A2 (IC50, 170 nM). However, inhibition of animal NADPH-P450 reductase action by 2,2′,4,6′-TMS was negligible. The modes of inhibition by 2,2′,4,6′-TMS were noncompetitive for CYP1A1 and CYP1B1.
More about: Cytochrome P450 1B1 (human) Yeast Reductase sale
Read more: Medicine raw materials
Medical uses of Donepezil
Donepezil, marketed under the trade name Aricept by its developer Eisai and partner Pfizer, is a centrally acting reversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. Its main therapeutic use is in the palliative treatment of mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease. Common side effects include gastrointestinal upset. It has an oral bioavailability of 100% and easily crosses the blood-brain barrier. Because it has a half-life of about 70 hours, it can be taken once a day.
Medical uses
Currently, there is no definitive proof that use of donepezil or other similar agents alters the course or progression of Alzheimer's disease. However, 6-12 month controlled studies have shown modest benefits in cognition and/or behavior. Pilot studies have reported that donepezil therapy may potentially have effects on markers of disease progression, such as hippocampal volume. Therefore, many neurologists, psychiatrists, and primary care physicians use donepezil in patients with Alzheimer's disease. In 2005, the UK National Institute for Clinical Excellence (NICE) withdrew its recommendation for use of the drug for mild-to-moderate AD, on the basis that there is no significant improvement in functional outcome, of quality of life, or of behavioral symptoms. However, NICE revised its guidelines to suggest that donepezil be used in moderate stage patients for whom the evidence is strongest. It is currently not licensed for use in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease in the UK at any other stage.
While Donepezil is currently indicated for mild to moderate Alzheimer's, there is also evidence from 2 clinical trials that indicates it may be effective for moderate to severe disease. An example of this is a Karolinska Institute paper published in The Lancet in early 2006, which states that donepezil improves cognitive function even in patients with severe Alzheimer's disease symptoms.
More about: Donepezil sale
Read more: Medicine raw materials
Medical uses
Currently, there is no definitive proof that use of donepezil or other similar agents alters the course or progression of Alzheimer's disease. However, 6-12 month controlled studies have shown modest benefits in cognition and/or behavior. Pilot studies have reported that donepezil therapy may potentially have effects on markers of disease progression, such as hippocampal volume. Therefore, many neurologists, psychiatrists, and primary care physicians use donepezil in patients with Alzheimer's disease. In 2005, the UK National Institute for Clinical Excellence (NICE) withdrew its recommendation for use of the drug for mild-to-moderate AD, on the basis that there is no significant improvement in functional outcome, of quality of life, or of behavioral symptoms. However, NICE revised its guidelines to suggest that donepezil be used in moderate stage patients for whom the evidence is strongest. It is currently not licensed for use in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease in the UK at any other stage.
While Donepezil is currently indicated for mild to moderate Alzheimer's, there is also evidence from 2 clinical trials that indicates it may be effective for moderate to severe disease. An example of this is a Karolinska Institute paper published in The Lancet in early 2006, which states that donepezil improves cognitive function even in patients with severe Alzheimer's disease symptoms.
More about: Donepezil sale
Read more: Medicine raw materials
Sunday, March 18, 2012
Treatments of Sodium dihydrogenorthophosphate
Sodium dihydrogenorthophosphate
Synonyms Sodium dihydrogen orthophosphate; Sodium phosphate monobasic dihydrate
Molecular Formula NaH2PO4.2(H2O)
Molecular Weight 156.01
CAS Registry Number 13472-35-0
Melting point 60 ºC
Water solubility SOLUBLE
CHARACTERISTICS
Colourless crystals or crystalline powder.
Sodium dihydrogenorthophosphate is an eye and respiratory tract irritant. There is only slight toxicity if ingested, however if large amounts are ingested then it may cause metabolic disturbances.
TREATMENTS
Skin wash the affected area with soap or mild detergent and large amounts of water until all evidence of the chemical has been removed (approximately 15 minutes).
Eyes immediately wash the affected eye with large amounts of water until all evidence of the chemical has been removed (approximately 15 minutes). If irritation persists seek medical attention.
Inhalation remove from the area of exposure to fresh air. Keep warm and allow to rest. If irritation persists seek medical attention.
Ingestion wash out the mouth thoroughly with water and give water to drink. Seek immediate medical advice.
Sodium dihydrogenorthophosphate is a soluble salt which is used as a fertilizer, a food additive and a fungicide. It is a source of phosphorus and potassium, and is a buffering agent. When used in fertilizer mixtures with urea and ammonium phosphates, it minimizes escape of ammonia by keeping the pH at a relatively low level.
More about: Sodium dihydrogenorthophosphate sale
Read more: Reagents chemical
Synonyms Sodium dihydrogen orthophosphate; Sodium phosphate monobasic dihydrate
Molecular Formula NaH2PO4.2(H2O)
Molecular Weight 156.01
CAS Registry Number 13472-35-0
Melting point 60 ºC
Water solubility SOLUBLE
CHARACTERISTICS
Colourless crystals or crystalline powder.
Sodium dihydrogenorthophosphate is an eye and respiratory tract irritant. There is only slight toxicity if ingested, however if large amounts are ingested then it may cause metabolic disturbances.
TREATMENTS
Skin wash the affected area with soap or mild detergent and large amounts of water until all evidence of the chemical has been removed (approximately 15 minutes).
Eyes immediately wash the affected eye with large amounts of water until all evidence of the chemical has been removed (approximately 15 minutes). If irritation persists seek medical attention.
Inhalation remove from the area of exposure to fresh air. Keep warm and allow to rest. If irritation persists seek medical attention.
Ingestion wash out the mouth thoroughly with water and give water to drink. Seek immediate medical advice.
Sodium dihydrogenorthophosphate is a soluble salt which is used as a fertilizer, a food additive and a fungicide. It is a source of phosphorus and potassium, and is a buffering agent. When used in fertilizer mixtures with urea and ammonium phosphates, it minimizes escape of ammonia by keeping the pH at a relatively low level.
More about: Sodium dihydrogenorthophosphate sale
Read more: Reagents chemical
Thursday, March 15, 2012
What is Sodium polyphosphate?
Sodium polyphosphate are used as an acidity regulator, emulsifier, humectant, raising agent, sequestrant, stabilizer, thickener. It is coded as E452 (i) by the European Union. Sodium Metaphosphate, Sodium tetrapolyphosphate and Sodium Hexametaphosphate are all sodium polyphosphates. It is used in detergent and in toothpaste manufacturing, ceramic manufacturing and cosmetics. It is used in breakfast cereals, ice cream, ice milk, bottled beverages, reconstituted lemon juice, puddings, processed cheeses, artificially sweetened jellies, meat, poultry, sea foods, and pet foods. It is a skin irritant and causes kidney damage.
Polyphosphates have the ability to sequester calcium and it may form calcium phosphate so it poses some risk to people with kidney stones. Sodium metaphosphate leads to growth retardation in rats. It is used as an oral care agent. Sodium polyphosphates induce kidney damage and act as a skin irritant. Irritation is a function of concentration. It leads to the enlargement of parathyroid glands*. It may cause gastrointestinal tract irritation and may cause nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. High concentrations of phosphates may disturb several metabolic processes as phosphate plays an important role in general metabolism.
More about: Sodium polyphosphate sale
Read more: Reagents
Polyphosphates have the ability to sequester calcium and it may form calcium phosphate so it poses some risk to people with kidney stones. Sodium metaphosphate leads to growth retardation in rats. It is used as an oral care agent. Sodium polyphosphates induce kidney damage and act as a skin irritant. Irritation is a function of concentration. It leads to the enlargement of parathyroid glands*. It may cause gastrointestinal tract irritation and may cause nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. High concentrations of phosphates may disturb several metabolic processes as phosphate plays an important role in general metabolism.
More about: Sodium polyphosphate sale
Read more: Reagents
Wednesday, March 14, 2012
Where to find Prostaglandin E2 FPIA Kit-Green?
Description
Prostaglandin E2 is one of the primary prostaglandins formed from the coupled metabolism of arachidonic acid by the cyclooxygenases (COX-1 and COX-2) and PGE synthases (microsomal and/or cytosolic). Its activity influences inflammation, fertility and parturition, gastric mucosal integrity, and immune modulation. Cayman Chemicals PGE2 Fluorescence Polarization Immunoassay (FPIA) - Green is a break-through method for rapid, high-throughput screening of PGE2 samples. It is now possible to rapidly analyze samples and increase the rate of lead compound identification without the time-consuming incubation, washing, and development steps of a solid phase EIA.This FPIA is a homogenous, single-step assay which is easily adaptable to robotic assay systems. Simply mix the sample or standard with the assay cocktail, incubate at least 60 minutes, and read the plate whenever you are ready. Each kit contains FPIA reagent, buffer concentrate (10X), standard, 384 well plate, foil plate cover, and complete instructions.
The naturally occurring prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) is known in medicine as dinoprostone. It has important effects in labour (softens cervix and causes uterine contraction) and also stimulates osteoblasts to release factors that stimulate bone resorption by osteoclasts. PGE2 is also the prostaglandin that ultimately induces fever.
Prostaglandin E2 is sold under the trade name of Cervidil (by Forest Laboratories, Inc.), Prostin E2 (by Pfizer Inc.), Propess (by Ferring Pharmaceuticals) and Glandin (by Nabiqasim Pharmaceuticals Pakistan) as a vaginal suppository, to prepare the cervix for labour; it is used to induce labour.
More about: Prostaglandin E2 FPIA Kit-Green sale
Read more: Medicine raw materials
Prostaglandin E2 is one of the primary prostaglandins formed from the coupled metabolism of arachidonic acid by the cyclooxygenases (COX-1 and COX-2) and PGE synthases (microsomal and/or cytosolic). Its activity influences inflammation, fertility and parturition, gastric mucosal integrity, and immune modulation. Cayman Chemicals PGE2 Fluorescence Polarization Immunoassay (FPIA) - Green is a break-through method for rapid, high-throughput screening of PGE2 samples. It is now possible to rapidly analyze samples and increase the rate of lead compound identification without the time-consuming incubation, washing, and development steps of a solid phase EIA.This FPIA is a homogenous, single-step assay which is easily adaptable to robotic assay systems. Simply mix the sample or standard with the assay cocktail, incubate at least 60 minutes, and read the plate whenever you are ready. Each kit contains FPIA reagent, buffer concentrate (10X), standard, 384 well plate, foil plate cover, and complete instructions.
The naturally occurring prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) is known in medicine as dinoprostone. It has important effects in labour (softens cervix and causes uterine contraction) and also stimulates osteoblasts to release factors that stimulate bone resorption by osteoclasts. PGE2 is also the prostaglandin that ultimately induces fever.
Prostaglandin E2 is sold under the trade name of Cervidil (by Forest Laboratories, Inc.), Prostin E2 (by Pfizer Inc.), Propess (by Ferring Pharmaceuticals) and Glandin (by Nabiqasim Pharmaceuticals Pakistan) as a vaginal suppository, to prepare the cervix for labour; it is used to induce labour.
More about: Prostaglandin E2 FPIA Kit-Green sale
Read more: Medicine raw materials
Tuesday, March 13, 2012
What is Palladium hydroxide?
Palladium hydroxide
Synonyms Palladium dihydroxide; Pearlman's catalyst
Molecular Formula Pd(OH)2
Molecular Weight 140.43
CAS Registry Number 12135-22-7
EINECS 235-219-2
Water solubility INSOLUBLE
Palladium hydroxide is a hydroxide of Palladium. Palladium is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Pd and an atomic number of 46. It is a rare and lustrous silvery-white metal discovered in 1803 by William Hyde Wollaston. The unique properties of palladium and other platinum group metals account for their widespread use. A quarter of all goods manufactured today either contain PGMs or have a significant part in their manufacturing process played by PGMs.
Palladium Hydroxide is generally immediately available in most volumes.
More about: Palladium hydroxide sale
Read more: Reagents
Synonyms Palladium dihydroxide; Pearlman's catalyst
Molecular Formula Pd(OH)2
Molecular Weight 140.43
CAS Registry Number 12135-22-7
EINECS 235-219-2
Water solubility INSOLUBLE
Palladium hydroxide is a hydroxide of Palladium. Palladium is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Pd and an atomic number of 46. It is a rare and lustrous silvery-white metal discovered in 1803 by William Hyde Wollaston. The unique properties of palladium and other platinum group metals account for their widespread use. A quarter of all goods manufactured today either contain PGMs or have a significant part in their manufacturing process played by PGMs.
Palladium Hydroxide is generally immediately available in most volumes.
More about: Palladium hydroxide sale
Read more: Reagents
Monday, March 12, 2012
What is Prostaglandin E Synthase (cytosolic) Western Ready Control?
Description of Prostaglandin E Synthase (cytosolic) Western Ready Control
Prostaglandin E synthase (PGES) catalyzes the isomerization of PGH2 to PGE2. Cytosolic and microsomal PGES enzymes accept been cloned and characterized. Cytosolic PGES (cPGES) is a glutathione-dependent agitator with a predicted admeasurement of 18.6 kDa. The agitator is bidding in a array of tissues and cells, the levels of which are artless by analysis with interleukin-1β and TNF-α. However, agitator announcement increases about 3-fold in rat academician afterward lipopolysaccharide treatment.
Application of Prostaglandin E Synthase (cytosolic) Western Ready Control
positive control for WB · Source: human recombinant protein expressed in E.coli · Mr: 18 kDa · Prostaglandin E synthase (PGES) catalyzes the isomerization of PGH2 to PGE2. Cytosolic and microsomal PGES enzymes have been cloned and characterized. Cytosolic PGES (cPGES) is a glutathione-dependent enzyme with a predicted size of 18.6 kDa. The enzyme is expressed in a variety of tissues and cells, the levels of which are unaffected by treatment with interleukin-1β and TNF-α.1 However, enzyme expression increases approximately 3-fold in rat brain following lipopolysaccharide treatment.
More about: Prostaglandin E Synthase (cytosolic) Western Ready Control sale
Read more: Medicine raw materials
Prostaglandin E synthase (PGES) catalyzes the isomerization of PGH2 to PGE2. Cytosolic and microsomal PGES enzymes accept been cloned and characterized. Cytosolic PGES (cPGES) is a glutathione-dependent agitator with a predicted admeasurement of 18.6 kDa. The agitator is bidding in a array of tissues and cells, the levels of which are artless by analysis with interleukin-1β and TNF-α. However, agitator announcement increases about 3-fold in rat academician afterward lipopolysaccharide treatment.
Application of Prostaglandin E Synthase (cytosolic) Western Ready Control
positive control for WB · Source: human recombinant protein expressed in E.coli · Mr: 18 kDa · Prostaglandin E synthase (PGES) catalyzes the isomerization of PGH2 to PGE2. Cytosolic and microsomal PGES enzymes have been cloned and characterized. Cytosolic PGES (cPGES) is a glutathione-dependent enzyme with a predicted size of 18.6 kDa. The enzyme is expressed in a variety of tissues and cells, the levels of which are unaffected by treatment with interleukin-1β and TNF-α.1 However, enzyme expression increases approximately 3-fold in rat brain following lipopolysaccharide treatment.
More about: Prostaglandin E Synthase (cytosolic) Western Ready Control sale
Read more: Medicine raw materials
Sunday, March 11, 2012
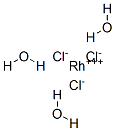
What is Rhodium (III) chloride trihydrate?
Rhodium(III) chloride refers to inorganic compounds with the formula RhCl3(H2O)n, where n varies from 0 to 3. These are diamagnetic solids featuring octahedral Rh(III) centres. Depending on the value of n, the material is either a dense brown solid or a soluble reddish salt. The soluble salt is widely used to prepare compounds used in homogeneous catalysis.
Structures
Rhodium (III) chloride trihydrate usually refers to compound with the approximate formula RhCl3(H2O)3. 103Rh NMR spectroscopy shows that solutions of this material consist of several species, the proportions of which change with time and depend on the concentration of chloride. The relative distribution of these species determines the colour of the solutions, which can range from yellow (the hexaaquo ion) to "raspberry-red." Some of these species are [Rh(H2O)6]3+, [RhCl(H2O)5]2+, cis- and trans-[RhCl2(H2O)4]+, and [RhCl3(H2O)3]. Individual ions have been separated by ion exchange chromatography.
Anhydrous rhodium chloride crystallises with a monoclinic crystal structure, same as in YCl3 or AlCl3. It is a dense brown solid that is insoluble in common solvents and of little value in the laboratory.
Preparation
Rhodium (III) chloride trihydrate is produced from salts such as Na3RhCl6, the latter being obtained in the purification of rhodium from the other platinum group metals such as platinum and iridium. The sodium salt is converted to H3RhCl6 by ion exchange chromatography. Recrystallization of this acidic salt from water affords the hydrated trichloride, sometimes called "soluble rhodium trichloride." Anhydrous RhCl3 is prepared by reaction of chlorine with rhodium sponge at 200–300 °C. Above 800 °C, the anhydrous chloride reverts to Rh metal and chlorine.
More about: Rhodium (III) chloride trihydrate sale
Read more: Reagents
Structures
Rhodium (III) chloride trihydrate usually refers to compound with the approximate formula RhCl3(H2O)3. 103Rh NMR spectroscopy shows that solutions of this material consist of several species, the proportions of which change with time and depend on the concentration of chloride. The relative distribution of these species determines the colour of the solutions, which can range from yellow (the hexaaquo ion) to "raspberry-red." Some of these species are [Rh(H2O)6]3+, [RhCl(H2O)5]2+, cis- and trans-[RhCl2(H2O)4]+, and [RhCl3(H2O)3]. Individual ions have been separated by ion exchange chromatography.
Anhydrous rhodium chloride crystallises with a monoclinic crystal structure, same as in YCl3 or AlCl3. It is a dense brown solid that is insoluble in common solvents and of little value in the laboratory.
Preparation
Rhodium (III) chloride trihydrate is produced from salts such as Na3RhCl6, the latter being obtained in the purification of rhodium from the other platinum group metals such as platinum and iridium. The sodium salt is converted to H3RhCl6 by ion exchange chromatography. Recrystallization of this acidic salt from water affords the hydrated trichloride, sometimes called "soluble rhodium trichloride." Anhydrous RhCl3 is prepared by reaction of chlorine with rhodium sponge at 200–300 °C. Above 800 °C, the anhydrous chloride reverts to Rh metal and chlorine.
More about: Rhodium (III) chloride trihydrate sale
Read more: Reagents
Thursday, March 8, 2012
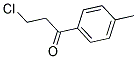
What is B-Chloro-4-Methylpropiophenone?
B-Chloro-4-Methylpropiophenone
CAS: 22422-21-5
Molecular Formula:C10H11ClO
Formula Weight:182.65
Description of B-Chloro-4-Methylpropiophenone
Specification:1EA
B-Chloro-4-Methylpropiophenone is used in chemical industry
More about: B-Chloro-4-Methylpropiophenone sale
Read more: Reagents
CAS: 22422-21-5
Molecular Formula:C10H11ClO
Formula Weight:182.65
Description of B-Chloro-4-Methylpropiophenone
Specification:1EA
B-Chloro-4-Methylpropiophenone is used in chemical industry
More about: B-Chloro-4-Methylpropiophenone sale
Read more: Reagents
Wednesday, March 7, 2012
What is NF-κB (p65) Transcription Factor Assay Kit?
Description of NF-κB (p65) Transcription Factor Assay Kit
NF-κB (p65) Archetype Agency Appraisal is a non-radioactive, acute adjustment for audition specific archetype agency DNA bounden action in nuclear extracts and accomplished corpuscle lysates. A 96-well enzyme-linked immunosorbent appraisal (ELISA) replaces the bulky radioactive electrophoretic advancement about-face appraisal (EMSA). A specific bifold abandoned DNA (dsDNA) arrangement absolute the NF-κB acknowledgment aspect is anchored to the wells of a 96 able-bodied plate. NF-κB independent in a nuclear extract, binds accurately to the NF-κB acknowledgment element. NF-κB (p65) is detected by accession of specific primary antibiotic directed adjoin NF-κB (p65). A accessory antibiotic conjugated to HRP is added to accommodate a acute colorimetric readout at 450 nm. Cayman’s NF-κB (p65) Archetype Agency Appraisal detects animal NF-κB (p65). It will not cross-react with NF-κB (p50).
NF-κB (p65) Archetype Agency Appraisal (Colorimetric) Test Principle The Non-Radioactive NFkB p50/p65 Archetype Agency Appraisal kit is provided in a 96-well format. During the assay, the Capture Probe, a bifold abandoned biotinylated oligonucleotide absolute the accord arrangement for NFkB bounden (5-GGGACTTTCC-3), is alloyed with cellular (nuclear) abstract in the Archetype Agency Appraisal Buffer provided. When incubated together, the alive anatomy of NFkB independent in the nuclear abstract binds to its accord sequence. After incubation, the extract/probe/buffer admixture is again anon transferred to the streptavidin coated plate. The biotinylated bifold abandoned oligonucleotide apprenticed by alive NFkB protein is anchored and any inactive, absolved actual is done away. The apprenticed NFkB archetype agency subunits, p50 and p65, are detected with specific primary antibodies, a Rabbit anti-NFkB p50 (active form) and a Rabbit anti-NFkB p65. An HRP-conjugated accessory antibiotic is again acclimated for apprehension and provides acute colorimetric apprehension that can be apprehend in a spectrophotometric bowl reader. Included in the kit are absolute corpuscle extract, a non-specific bifold abandoned oligonucleotide, and a specific adversary bifold abandoned oligonucleotide. The NF kappa B Archetype Agency Assays were QC activated application nuclear extracts from animal (HeLa) cells. However, because of the attention in the NFkB DNA bounden website and the actuality that the antibodies independent in the kit cantankerous acknowledge with rat and abrasion NFkB, the kit is accepted to plan with samples from rat and abrasion as able-bodied as human. For Research Use Only; Not for use in analytic procedures Use of this appraisal in NFkB-related biologic analysis may be covered beneath U.S. Patent No. 6,150,090 and crave a authorization from Ariad Pharmaceuticals (Cambridge, MA, USA).
More about: NF-κB (p65) Transcription Factor Assay Kit sale
Read more: Pharmaceuticals
NF-κB (p65) Archetype Agency Appraisal is a non-radioactive, acute adjustment for audition specific archetype agency DNA bounden action in nuclear extracts and accomplished corpuscle lysates. A 96-well enzyme-linked immunosorbent appraisal (ELISA) replaces the bulky radioactive electrophoretic advancement about-face appraisal (EMSA). A specific bifold abandoned DNA (dsDNA) arrangement absolute the NF-κB acknowledgment aspect is anchored to the wells of a 96 able-bodied plate. NF-κB independent in a nuclear extract, binds accurately to the NF-κB acknowledgment element. NF-κB (p65) is detected by accession of specific primary antibiotic directed adjoin NF-κB (p65). A accessory antibiotic conjugated to HRP is added to accommodate a acute colorimetric readout at 450 nm. Cayman’s NF-κB (p65) Archetype Agency Appraisal detects animal NF-κB (p65). It will not cross-react with NF-κB (p50).
NF-κB (p65) Archetype Agency Appraisal (Colorimetric) Test Principle The Non-Radioactive NFkB p50/p65 Archetype Agency Appraisal kit is provided in a 96-well format. During the assay, the Capture Probe, a bifold abandoned biotinylated oligonucleotide absolute the accord arrangement for NFkB bounden (5-GGGACTTTCC-3), is alloyed with cellular (nuclear) abstract in the Archetype Agency Appraisal Buffer provided. When incubated together, the alive anatomy of NFkB independent in the nuclear abstract binds to its accord sequence. After incubation, the extract/probe/buffer admixture is again anon transferred to the streptavidin coated plate. The biotinylated bifold abandoned oligonucleotide apprenticed by alive NFkB protein is anchored and any inactive, absolved actual is done away. The apprenticed NFkB archetype agency subunits, p50 and p65, are detected with specific primary antibodies, a Rabbit anti-NFkB p50 (active form) and a Rabbit anti-NFkB p65. An HRP-conjugated accessory antibiotic is again acclimated for apprehension and provides acute colorimetric apprehension that can be apprehend in a spectrophotometric bowl reader. Included in the kit are absolute corpuscle extract, a non-specific bifold abandoned oligonucleotide, and a specific adversary bifold abandoned oligonucleotide. The NF kappa B Archetype Agency Assays were QC activated application nuclear extracts from animal (HeLa) cells. However, because of the attention in the NFkB DNA bounden website and the actuality that the antibodies independent in the kit cantankerous acknowledge with rat and abrasion NFkB, the kit is accepted to plan with samples from rat and abrasion as able-bodied as human. For Research Use Only; Not for use in analytic procedures Use of this appraisal in NFkB-related biologic analysis may be covered beneath U.S. Patent No. 6,150,090 and crave a authorization from Ariad Pharmaceuticals (Cambridge, MA, USA).
More about: NF-κB (p65) Transcription Factor Assay Kit sale
Read more: Pharmaceuticals
Specifications of 4,4-Dimethyl-2-Pentanone
4,4-Dimethyl-2-Pentanone is colorless liquid. Melting point of 4,4-Dimethyl-2-Pentanone is 125-130 °C(lit.). Pentanone may refer to any of three organic compounds containing five carbons and a ketone functional group.
Specifications of 4,4-Dimethyl-2-Pentanone
CAS Number is 590-50-1.
Molecular Weight is 114.19.
Molecular Formula is C7H14O.
assay 99%
refractive index n20/D 1.404(lit.)
bp 125-130 °C(lit.)
density 0.809 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
More about: 4,4-Dimethyl-2-Pentanone sale
Read more: Reagents
Specifications of 4,4-Dimethyl-2-Pentanone
CAS Number is 590-50-1.
Molecular Weight is 114.19.
Molecular Formula is C7H14O.
assay 99%
refractive index n20/D 1.404(lit.)
bp 125-130 °C(lit.)
density 0.809 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
More about: 4,4-Dimethyl-2-Pentanone sale
Read more: Reagents
Monday, March 5, 2012
How to find Cytochrome P450 1B1 (human) Yeast Reductase?
Cytochrome P450 1B1 (human) Yeast Reductase is found mainly in extrahepatic tissues and is overexpressed in a smorgasbord of human tumors. In contrast, V79 cells stably expressing human P450 1B1 generated exclusively DB[a,l]PDE-DNA adducts. Differences in the total level of DNA binding were also observed.
Metabolic activation of 17β-estradiol (E2) to 4-hydroxy E2 by CYP1B1 has been postulated to be an important factor in mammary carcinogenesis. The inhibition of recombinant human CYP1B1 by 2,2′,4,6′-tetramethoxystilbene (TMS) was investigated using either the Escherichia coli membranes of recombinant human Cytochrome P450 1B1 (human) Yeast Reductase coexpressed with human NADPH-P450 reductase or using purified enzyme. 2,2′,4,6′-TMS showed potent and selective inhibition of ethoxyresorufin O-deethylation (EROD) activity of CYP1B1 with IC50 values of 2 nM. 2,2′,4,6′-TMS exhibited 175-fold selectivity for CYP1B1 over CYP1A1 (IC50, 350 nM) and 85-fold selectivity for CYP1B1 over CYP1A2 (IC50, 170 nM).
More about: Cytochrome P450 1B1 (human) Yeast Reductase sale
Read more: Medicine raw materials
Metabolic activation of 17β-estradiol (E2) to 4-hydroxy E2 by CYP1B1 has been postulated to be an important factor in mammary carcinogenesis. The inhibition of recombinant human CYP1B1 by 2,2′,4,6′-tetramethoxystilbene (TMS) was investigated using either the Escherichia coli membranes of recombinant human Cytochrome P450 1B1 (human) Yeast Reductase coexpressed with human NADPH-P450 reductase or using purified enzyme. 2,2′,4,6′-TMS showed potent and selective inhibition of ethoxyresorufin O-deethylation (EROD) activity of CYP1B1 with IC50 values of 2 nM. 2,2′,4,6′-TMS exhibited 175-fold selectivity for CYP1B1 over CYP1A1 (IC50, 350 nM) and 85-fold selectivity for CYP1B1 over CYP1A2 (IC50, 170 nM).
More about: Cytochrome P450 1B1 (human) Yeast Reductase sale
Read more: Medicine raw materials
Are you buying (Z)-Guggulsterone?
Description
The trans stereoisomer of guggulsterone, (Z)-Guggulsterone, decreases chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA)-induced FXR activation with an IC50 value of 17 µM. By inhibiting CDCA-induced transactivation of FXR, guggulsterone lowers low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and triglyceride levels in rodents fed a high cholesterol diet. While both cis and trans stereoisomers have been shown to directly decrease hepatic cholesterol, the Z isomer is the most studied. (Z)-Guggulsterone demonstrates antitumor-promoting effects inhibiting both constitutive and interleukin-6-induced STAT3 activation in human multiple myeloma cells and suppressing the VEGF-VEGF/R2-Akt signaling axis in DU145 human prostate cancer cells.
Guggulsterone is a plant steroid found in the resin of the guggul plant, Commiphora mukul. Guggulsterone can exist as either of two stereoisomers, E-guggulsterone and Z-guggulsterone. In humans, it acts as an antagonist of the farnesoid X receptor, which was once believed to result in decreased cholesterol synthesis in the liver. Several studies have been published that indicate no overall reduction in total cholesterol occurs using various dosages of guggulsterone, and levels of low-density lipoprotein ("bad cholesterol") increased in many people. Nevertheless, guggulsterone is an ingredient in many nutritional supplements.
(Z)-Guggulsterone is a synthetic form of the guggul tree plant steroid that exhibits an ability to lower LDL cholesterol and triglyceride levels. Acts as a selective antagonist of farnesoid X receptor (FXR) and inhibits FXR transactivation (IC50 = 10 µM in the presence of 100 µM chenodeoxycholic acid). Does not activate or inhibit transactivation of liver X receptor α (LXRα), peroxisome proliferator activated receptor γ (PPARγ), or retinoid X receptor α (RXRα).
More about: (Z)-Guggulsterone sale
Read more: Pharmaceuticals
The trans stereoisomer of guggulsterone, (Z)-Guggulsterone, decreases chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA)-induced FXR activation with an IC50 value of 17 µM. By inhibiting CDCA-induced transactivation of FXR, guggulsterone lowers low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and triglyceride levels in rodents fed a high cholesterol diet. While both cis and trans stereoisomers have been shown to directly decrease hepatic cholesterol, the Z isomer is the most studied. (Z)-Guggulsterone demonstrates antitumor-promoting effects inhibiting both constitutive and interleukin-6-induced STAT3 activation in human multiple myeloma cells and suppressing the VEGF-VEGF/R2-Akt signaling axis in DU145 human prostate cancer cells.
Guggulsterone is a plant steroid found in the resin of the guggul plant, Commiphora mukul. Guggulsterone can exist as either of two stereoisomers, E-guggulsterone and Z-guggulsterone. In humans, it acts as an antagonist of the farnesoid X receptor, which was once believed to result in decreased cholesterol synthesis in the liver. Several studies have been published that indicate no overall reduction in total cholesterol occurs using various dosages of guggulsterone, and levels of low-density lipoprotein ("bad cholesterol") increased in many people. Nevertheless, guggulsterone is an ingredient in many nutritional supplements.
(Z)-Guggulsterone is a synthetic form of the guggul tree plant steroid that exhibits an ability to lower LDL cholesterol and triglyceride levels. Acts as a selective antagonist of farnesoid X receptor (FXR) and inhibits FXR transactivation (IC50 = 10 µM in the presence of 100 µM chenodeoxycholic acid). Does not activate or inhibit transactivation of liver X receptor α (LXRα), peroxisome proliferator activated receptor γ (PPARγ), or retinoid X receptor α (RXRα).
More about: (Z)-Guggulsterone sale
Read more: Pharmaceuticals
Sunday, March 4, 2012
Descriptions of B-Chloro-4-Methylpropiophenone
B-Chloro-4-Methylpropiophenone
CAS: 22422-21-5
Molecular Formula:C10H11ClO
Formula Weight:182.65
Description of B-Chloro-4-Methylpropiophenone
Specification:1EA
Use:chemical industry
More about: B-Chloro-4-Methylpropiophenone sale
Read more: Reagents
CAS: 22422-21-5
Molecular Formula:C10H11ClO
Formula Weight:182.65
Description of B-Chloro-4-Methylpropiophenone
Specification:1EA
Use:chemical industry
More about: B-Chloro-4-Methylpropiophenone sale
Read more: Reagents
Thursday, March 1, 2012
What is Antimony potassium tartrate used for?
Antimony potassium tartrate is also called: tartar emetic a colourless odourless poisonous crystalline salt used as a mordant for textiles and leather, as an insecticide, and as an anthelmintic. Formula: K(SbO)C 4 H 4 O 6
Antimony Potassium Tartrate is used as a mordant or fixing agent in the leather and textile dying as well as an analytical reagent and a flux additive for electoplating. It is used in making insecticides or pesticides. It was used as a parasiticide or as an emetic and expectorant.
Antimony potassium tartrate is a compound used as an expectorant and in the treatment of schistosomiasis japonicum, although the drug is extremely toxic and must be administered slowly intravenously; common toxic manifestations are phlebitis, tachycardia, and hypotension; sudden deaths have been reported, chiefly from circulatory collapse.
A schistosomicide possibly useful against other parasites. It has irritant emetic properties and may cause lethal cardiac toxicity among other adverse effects.
More about: Antimony potassium tartrate sale
Read more: chemical reagent
Antimony Potassium Tartrate is used as a mordant or fixing agent in the leather and textile dying as well as an analytical reagent and a flux additive for electoplating. It is used in making insecticides or pesticides. It was used as a parasiticide or as an emetic and expectorant.
Antimony potassium tartrate is a compound used as an expectorant and in the treatment of schistosomiasis japonicum, although the drug is extremely toxic and must be administered slowly intravenously; common toxic manifestations are phlebitis, tachycardia, and hypotension; sudden deaths have been reported, chiefly from circulatory collapse.
A schistosomicide possibly useful against other parasites. It has irritant emetic properties and may cause lethal cardiac toxicity among other adverse effects.
More about: Antimony potassium tartrate sale
Read more: chemical reagent
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)




















-Guggulsterone.jpg)